Difference between revisions of "Encoder Support"
(Changed categories.) |
(Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:TD-044-078 ig42 motor encoders.jpg|thumb|191x191px|The encoder is inside the black end cap. Extra wires are present that connect with the encoder.|link=https://wiki.sdrobots.com/index.php/File:TD-044-078_ig42_motor_encoders.jpg]]Rotary encoders are devices that generate electrical pulses as they rotate. The angle or rate of rotation that the encoder is experiencing is measured by monitoring the number or frequency of the pulses. In robotics, encoders are most commonly attached to the robot's drive motors and used to measure the robot's linear speed, angular speed, and distance traveled. Drive motor encoders can also be used to perform [[Speed Control#Closed Loop|closed loop speed control]] on the wheels. More generally, encoders can be attached to any of the robot's joints to track its speed and/or angle, such as a rotating joint in a robotic arm. | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
Revision as of 12:31, 16 April 2021
Rotary encoders are devices that generate electrical pulses as they rotate. The angle or rate of rotation that the encoder is experiencing is measured by monitoring the number or frequency of the pulses. In robotics, encoders are most commonly attached to the robot's drive motors and used to measure the robot's linear speed, angular speed, and distance traveled. Drive motor encoders can also be used to perform closed loop speed control on the wheels. More generally, encoders can be attached to any of the robot's joints to track its speed and/or angle, such as a rotating joint in a robotic arm.
Contents
Summary
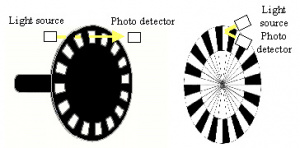
An encoder is a device attached to an actuator or motor that enables you to measure precise movements. The advantages of this are precision movements and speed control. There are two main types of encoders, hall-effect and optical. A hall-effect encoder typically uses an iron mass or magnet, the sensor then 'watches' for changes in the magnetic field. An optical encoder uses layered disks. The disks have symmetrical areas of transparent and opaque material that allows a light source, such as an LED to pass through and strike a photo detector.
Both types of encoders are fundamentally solid. Deciding between the two depends on your budget and your desired CPR (Counts Per Revolution). Hall-effect encoders tend to be less expensive but have a significantly lower CPR. This is not necessarily a bad thing. If you just want to know how far your robot has traveled you do not need the 1,000-2,000 counts for an optical encoder a 98 CPR for a hall-effect encoder provides more than enough resolution for you needs. A standard six inch tire has a circumference of approximately 18.8 inches. At a 98 CPR you have a resolution of 0.19 inches (a little over an eight of an inch). Typically an encoder is put on the motor, which is then geared down. So if you have a 1:10 reduction, your encoder now will read 0.019 inches per count.
Encoder Output
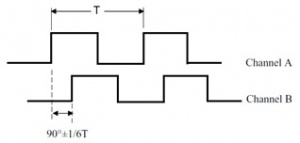
Encoders typically output what is known as a quadrature signal. A quadrature signal is comprised of two channels (Channel A and Channel B). Channel B is 90 degrees out of phase from channel A. This allows the circuitry watching the output signal to know what direction you are traveling. If B trails A then your motor is moving clockwise, if A trails B then your motor is moving counter clockwise.
Picture
Reading an Encoder
There are two basic ways of integrating an encoder into your design. The encoder can either feed back to your motor control circuit or your microcontroller circuit. For feeding the data back to the motor controller itself frees up your microcontroller for other tasks and is incredibly simple to implement. Take Dimension Engineering's Kangaroo x2 Motion Controller. The motion controller attaches to their Sabertooth and SyRen product line and automatically takes care of speed control functions for you. The disadvantage is that it takes your microcontroller out of the loop and misses out of that data so you cannot write a program to move the motor precisely 90 degrees because the microcontroller doesn't know where the motor is. The Kangaroo can be polled for the data, but that is typically not fast enough. Other motor controllers such as the RoboteQ's have encoders built in too.
The other option is to have the encoder output wired to your microcontroller circuit. It is possible to have it directly tied to your microcontroller but you will have to have it constantly sit there and check for the pulses. This will tie up your microcontroller so it will not be able to complete another function while the motor is moving. A solution for this is our LS7366R quadrature buffer breakout. The LS7366R takes care of watching for the encoder pulses and you simply send it a SPI command when you want to know where you are or to reset the encoder counts. This way you can receive precise encoder feedback without having to devote all of your resources to it.
Quick Links to our Encoders and Accessories:
Encoder Buffer and Pull-up Boards:
- Dual LS7366R Quadrature Encoder Buffer Breakout Board (TE-183-002)
- Kangaroo x2 motion controller (TE-180-000)
- IG32, IG42, and IG52 Gear Motor Encoder Pull-up Board (TE-179-000)
Motors with Encoders:
- IG42 24VDC 013 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-044-013)
- IG52-04 24VDC 082 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-045-082)
- IG32P 24VDC 075 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-055-075)
- IG32 24VDC 074 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-054-074)
- IG42 24VDC 078 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-044-078)
- IG32P 24VDC 265 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-055-265)
- IG32P 24VDC 190 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-055-190)
- IG32 24VDC 191 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-054-191)
- IG52-04 24VDC 010 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-045-010)
- IG52-04 24VDC 136 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-045-136)
- IG42 24VDC 122 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-044-122)
- IG52-04 24VDC 285 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-045-285)
- IG42 24VDC 240 RPM Gear Motor with Encoder (TD-044-240)
Motor Controllers with direct encoder feedback:
- SyRen 50A Regenerative Motor Driver (TE-098-150) with Kangaroo Option
- RoboteQ SDC2150 - 2x20A 50V Motor Controller with Encoder Input (TE-144-050)
- RoboteQ SDC2130 - 2x20A 30V Motor Controller with Encoder Input (TE-144-030)
- RoboteQ XDC2460 - 2x150A 60V Motor Controller with Encoder Input (TE-286-150)
- RoboteQ MDC2460 - 2x60A 60V Motor Controller with Encoder Input (TE-240-060)
- RoboteQ MDC2230 - 2x60A 30V Motor Controller with Encoder Input (TE-240-030)
- SyRen 25A Regenerative Motor Driver (TE-098-125) with Kangaroo Option
- SyRen 10A Regenerative Motor Driver (TE-098-110) with Kangaroo Option
- Sabertooth Dual 25A Motor Driver (TE-091-225) with Kangaroo Option
- Sabertooth Dual 60A motor driver (TE-091-260) with Kangaroo Option
Encoder support: