Difference between revisions of "Vectoring Robot Support"
(→Motors and Motor Mounts) (Tag: Visual edit) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Vectoring robots are robots that are able to add left/right strafing to their motion. In other words, vectoring robots can move sideways. Conventional wheeled mobile robots can only move forward and backwards and turn left/right. By adding the left and right strafing components, vectoring robots are able to move in any direction along the ground and turn left/right. This is accomplished by equipping special wheels and using a [[Electronic Control Units|microcontroller]] to calculate the motor speeds required for a commanded motion. | |
| − | == How Vectoring Movement is Possible == | + | ==How Vectoring Movement is Possible== |
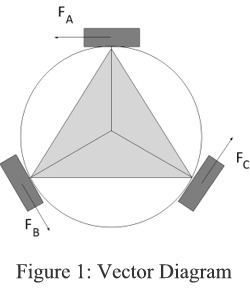
Vectoring movement is achieved through a sum of forces generated by each wheel. In Figure 1 below, you will notice that for the robot to move to the right motor A will need to move in the negative direction and motors B and C would move in the positive direction. | Vectoring movement is achieved through a sum of forces generated by each wheel. In Figure 1 below, you will notice that for the robot to move to the right motor A will need to move in the negative direction and motors B and C would move in the positive direction. | ||
This diagram also shows why motors B and C must be reduced while moving sideways. Motors B and C must have the same power to negate the forward and back movement while motor A must generate the same amount of sideways force as the sum of B and C. | This diagram also shows why motors B and C must be reduced while moving sideways. Motors B and C must have the same power to negate the forward and back movement while motor A must generate the same amount of sideways force as the sum of B and C. | ||
| + | [[File:vectorSupportPage1.jpg|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | |||
Figures 2 and 3 show the two distinct types of omni wheels. Both Omni wheels and Mecanum wheels provide traction in normal wheel movement as any other wheel would. however, what makes these wheels special are the small rollers along the wheel's edges. These wheels are designed to provide a minimum amount of friction sideways allowing the wheels to move in any direction. | Figures 2 and 3 show the two distinct types of omni wheels. Both Omni wheels and Mecanum wheels provide traction in normal wheel movement as any other wheel would. however, what makes these wheels special are the small rollers along the wheel's edges. These wheels are designed to provide a minimum amount of friction sideways allowing the wheels to move in any direction. | ||
| + | [[File:vectorSupportPage2.jpg|center|thumb]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Omni wheels have smaller rollers on the edges that move completely perpendicular to the wheel itself. With this type of wheel they must be mounted perpendicular to the center of the robot as seen in Figure 1. | Omni wheels have smaller rollers on the edges that move completely perpendicular to the wheel itself. With this type of wheel they must be mounted perpendicular to the center of the robot as seen in Figure 1. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 16: | ||
Mecanum wheels are unique in that the small rollers are at a 45 degree angle. This allows them to be mounted like normal wheels but provide the same style of movement as Omni wheels. | Mecanum wheels are unique in that the small rollers are at a 45 degree angle. This allows them to be mounted like normal wheels but provide the same style of movement as Omni wheels. | ||
| − | == 4WD Omni-directional Robots == | + | ==4WD Omni-directional Robots== |
| − | We have several options for four wheel omni-directional robots. They use mecanum wheels or omni wheels mounted at a 45 degree angle. By changing the speeds and directions of the wheels you can achieve movement in any direction! Due to the style of the wheels it is possible to move the wheels in a standard "tank style" motion to drive normally when needed. These robots also work well for supporting high payloads since the wheels allow them to turn with very low friction. See the load ratings on the robot page for an idea of the payload. | + | We have several options for four wheel omni-directional robots. They use mecanum wheels or omni wheels mounted at a 45 degree angle. By changing the speeds and directions of the wheels you can achieve movement in any direction! Due to the style of the wheels it is possible to move the wheels in a standard "tank style" motion to drive normally when needed. These robots also work well for supporting high payloads since the wheels allow them to turn with very low friction. See the load ratings on the robot page for an idea of the payload.{{#evt: |
| + | service=youtube | ||
| + | |id=https://youtu.be/Rt2Z3Sxtdn4 | ||
| + | |alignment=center | ||
| + | |dimensions=600 | ||
| + | }}'''4WD Vectoring Robot Platforms''' | ||
| − | + | *<sdr item id=1487> Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 DM</sdr item> | |
| + | *<sdr item id=1713> Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 SB</sdr item> | ||
| + | *<sdr item id=2263> Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG42 SB</sdr item> | ||
| + | *<sdr item id=1788> Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG52 DB</sdr item> | ||
| + | *<sdr item id=2270> Programmable Quad-Wheel Omni-Directional Vectoring Robot Kit - IG32 SB</sdr item> | ||
| − | + | ==3WD Omni-directional Robots== | |
| − | + | Our 3WD omni-directional robots use our double-row omni wheels, allowing them to vector in any direction. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == 3WD Omni-directional Robots == | ||
| − | Our 3WD omni-directional robots our double-row omni wheels, allowing | ||
'''3WD Vectoring Robot Platform''' | '''3WD Vectoring Robot Platform''' | ||
| − | * Programmable Tri-Wheel Vectoring Robot Kit - IG32 Medium Duty SB | + | *<sdr item id=2229>Programmable Tri-Wheel Vectoring Robot Kit - IG32 Medium Duty SB</sdr item> |
| − | * Programmable Triangular Omni Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 DM | + | *<sdr item id=1486>Programmable Triangular Omni Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 DM</sdr item> |
==Controls and Specifications== | ==Controls and Specifications== | ||
===Motors and Motor Mounts=== | ===Motors and Motor Mounts=== | ||
| − | We have mecanum wheel robot kits that use IG32, IG42, and IG52 motors. Below are the motors that we recommend using with these platforms, though you can use different motors if you need more speed or higher payloads. All motors are available in wide range of RPMs and some are available with a built in encoder option. For a detailed list of our available motors please see the link below. The Omni wheel based chassis is available in both IG32 and IG42 variants. | + | We have mecanum wheel robot kits that use IG32, IG42, and IG52 [[motors]]. Below are the motors that we recommend using with these platforms, though you can use different motors if you need more speed or higher payloads. All motors are available in wide range of RPMs and some are available with a built in [[Encoder Support|encoder]] option. For a detailed list of our available motors please see the link below. The Omni wheel based chassis is available in both IG32 and IG42 variants. |
'''Suggested Motors''' | '''Suggested Motors''' | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=374> 32mm 190 RPM 24V IG32 Gear Motor (TD-015-190)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=374> 42mm 240 RPM 24V IG42 Gear Motor (TD-016-240)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=872> 52mm 136 RPM 24V IG52 Gear Motor (TD-048-136)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2109> IG32 or IG42 Motor Mount Tube for Omni Wheel Chassis (TD-056-342)</sdr item> |
'''Motor Hookups''' | '''Motor Hookups''' | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=387> Electric Motor Hookup Kits (TE-024-000)</sdr item> |
| − | * [[Motor Wiring Support|Electric Motor Wiring Support]] | + | *[[Motor Wiring Support|Electric Motor Wiring Support]] |
Click here for a listing of our available motors. | Click here for a listing of our available motors. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
Our Mecanum wheels are available stand-alone or paired with compatible wheel hubs. All wheels listed below fit any of the nexus aluminum hubs. The 4" mecanum wheels also fit the SDR manufactured flush mounted hubs. | Our Mecanum wheels are available stand-alone or paired with compatible wheel hubs. All wheels listed below fit any of the nexus aluminum hubs. The 4" mecanum wheels also fit the SDR manufactured flush mounted hubs. | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1352> 4 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel - Ball Bearing(TD-090-100)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2062> 4 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel - Sleeve Bearing(TD-169-100)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2058> 6 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel (TD-090-152)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1351> 8 inch Nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel (TD-090-203)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1488> SDR Flush Mounted Hub with 6mm Bore (TD-107-006)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1489> SDR Flush Mounted Hub with 8mm Bore (TD-107-008)</sdr item> |
Nexus Aluminum Hubs | Nexus Aluminum Hubs | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1359> 6mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-006)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1358> 8mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-008)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1378> 12mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-012)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1379> 0.5" Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-050)</sdr item> |
The Omni wheels are shafts are sold together as one unit. The shaft comes with a bearing and lock collar that fit into/onto the motors and motor mounts. The wheels are 4 inch in diameter. The traction wheels are made of durable urethane to help grip the floor. The wheels are available in two types; single row and double row. The double row wheels provide smoother operation but both work great. | The Omni wheels are shafts are sold together as one unit. The shaft comes with a bearing and lock collar that fit into/onto the motors and motor mounts. The wheels are 4 inch in diameter. The traction wheels are made of durable urethane to help grip the floor. The wheels are available in two types; single row and double row. The double row wheels provide smoother operation but both work great. | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1734> Nexus Omni-Wheel and Shaft Assembly - 6mm Bore (TD-145-006)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2291> Nexus Omni-Wheel and Shaft Assembly - 8mm Bore (TD-145-008)</sdr item> |
===Mecanum Wheels=== | ===Mecanum Wheels=== | ||
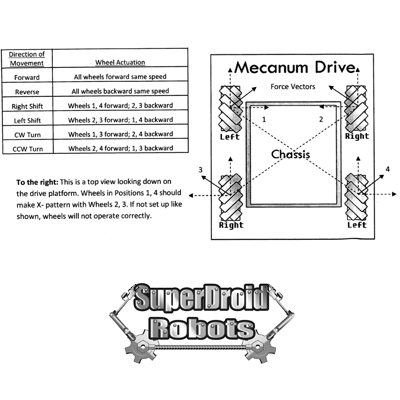
Below is a diagram showing how the mecanum wheels should be mounted and which direction to turn the wheels for vectoring movements. | Below is a diagram showing how the mecanum wheels should be mounted and which direction to turn the wheels for vectoring movements. | ||
| − | + | [[File:mecanum drive wheels vectoring robot tn.jpg|center|thumb|400x400px]] | |
| − | + | <br /> | |
===Motor and Speed Controllers=== | ===Motor and Speed Controllers=== | ||
| − | We offer a variety of motor controllers to allow for simple operation of the robot. The motor controllers are independent of the chassis type (Mecanum or Omni). To provide vectoring movement it is required to have one motor channel per motor. | + | [[File:Roboclaw 2x15 Motor Controller.jpg|thumb|250x250px|<sdr item id=2627>RoboClaw 2x15 Motor Controller</sdr item>]] |
| + | We offer a variety of [[Motor Controller Support|motor controllers]] to allow for simple operation of the robot. The motor controllers are independent of the chassis type (Mecanum or Omni). To provide vectoring movement it is required to have one motor channel per motor. Higher amperage motor controllers will be needed as the motor size and payload of the robot increases. | ||
| − | + | For the best vectoring performance, use motors with [[Encoder Support|encoders]] and a motor controller that has [[Speed Control#Closed Loop|closed loop speed control]], such as a Roboteq or Roboclaw. To vector cleanly in a desired direction, the robot's wheels must rotate at precise speed ratios relative to one another. If the ratios are off, then the movement will be sloppy -- e.g. instead of strafing purely to the right the robot might also drift slightly forward and turn slightly left during the movement. Closed loop speed control mitigates this effect so the robot moves as commanded. | |
| − | + | Dimension Engineering's motor controllers are versatile and reliable options when no closed loop speed control is needed. | |
'''Recommended Motor Controllers''' | '''Recommended Motor Controllers''' | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2627>RoboClaw 2x15A (TE-331-215)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2629>RoboClaw 2x30A (TE-331-230)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2628>RoboClaw Solo 30A Motor Controller (TE-331-130)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1826>RoboteQ SDC2160 2x20A (TE-144-060)</sdr item> |
| − | + | *<sdr item id=847>SyRen 10 (TE-098-110)</sdr item> | |
| + | *<sdr item id=822>Sabertooth Dual 25A (TE-091-225)</sdr item> | ||
| + | *<sdr item id=1822>Sabertooth Dual 32A (TE-091-232)</sdr item> | ||
===Controller and Controller Interface=== | ===Controller and Controller Interface=== | ||
| − | We offer three main control options for vectoring robots: Radio Controlled, WiFi, and wireless serial (xBee). | + | We offer three main [[Control System|control options]] for vectoring robots: Radio Controlled, WiFi, and wireless serial (xBee). |
'''R/C (Radio Control)''' | '''R/C (Radio Control)''' | ||
| − | For R/C control of the robot, although the motor controllers listed above support RC you will still need a | + | For [[Control System#Analog|R/C control]] of the robot, although the motor controllers listed above support RC you will still need a [[Electronic Control Units|microcontroller]] on the robot in order to handle the motor mixing necessary to achieve vectoring motion. |
For accurate robot control, the remote will require at least a two axis joystick/control and a signal switch to change driving modes if desired. Below is a recommended listing of our R/C remotes. | For accurate robot control, the remote will require at least a two axis joystick/control and a signal switch to change driving modes if desired. Below is a recommended listing of our R/C remotes. | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2617> FLYSKY FS-i6 2.4G 6CH Transmitter & Receiver (TE-328-000)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=2672> Spektrum DSMX DX6e Transmitter with AR620 Receiver (TE-336-DX6)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=1135> Spektrum DSMX DX8 8-Channel Transmitter Gen 2 with AR8010T Receiver (TE-113-008)</sdr item> |
'''WiFi Control''' | '''WiFi Control''' | ||
| − | + | We offer an Arduino-based <sdr item id=1440>Wifi control interface package (TE-900-003)</sdr item> that includes an <sdr item id=1292>Arduino Mega</sdr item>, <sdr item id=1419>SDR Breakout shield</sdr item>, Raspberry Pi, voltage regulators, and a <sdr item id=1913>4 channel TTL Relay Board (TE-010-405)</sdr item>. The control package also comes with the source code for the control software and the Arduino firmware needed for operation of the robot. | |
| − | + | Please see our [[Wi-Fi Robots|WiFi Control Interface Support Page]] for more information. | |
| − | |||
| − | Please see our WiFi Control Interface Support Page for more information. | ||
'''Wireless Serial Control''' | '''Wireless Serial Control''' | ||
| − | Wireless serial control is achieved through an xBee radio. Wireless serial is currently only available if you choose an Arduino based control system. The xBee radio connects to the Arduino through the Arduino Wireless SD Shield (MCU-064-000). A Wireless Serial Control system is available by request. Please contact us for more information. | + | Wireless serial control is achieved through an xBee radio. Wireless serial is currently only available if you choose an Arduino-based control system. The xBee radio connects to the Arduino through the Arduino Wireless SD Shield (MCU-064-000). A Wireless Serial Control system is available by request. Please contact us for more information. |
| − | Please see our Wireless Serial Support Page for more information. | + | Please see our [[XBee Wireless Serial Module|Wireless Serial Support Page]] for more information. |
===Hardware=== | ===Hardware=== | ||
The final item you need to make your kit complete is a hardware package. It includes nuts, bolts, washers, cable ties, and cable hold downs. | The final item you need to make your kit complete is a hardware package. It includes nuts, bolts, washers, cable ties, and cable hold downs. | ||
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=401> Hardware Package (mounts most components to the base robot) (TD-021-000)</sdr item> |
| − | * | + | *<sdr item id=399> Servo Standoff Mounting Hardware (TD-024-000)</sdr item> |
===Sensors=== | ===Sensors=== | ||
| − | In order to make your robot autonomous, you will need to add sensors. Sensors can always be added or removed at a later date but always be mindful of how the sensors interact with your | + | In order to make your robot [[:Category:Autonomous|autonomous]], you will need to add [[:Category:Sensors|sensors]]. Sensors can always be added or removed at a later date but always be mindful of how the sensors interact with your microcontroller. Some sensors operate under I2C, some SPI and some analog. See our [[:Category:Sensors|Sensor Support Page]] for more information. |
| + | |||
| + | *Accelerometers, Gyros, GPS, and Compasses | ||
| + | *Contact Sensors | ||
| + | *Current Sensors | ||
| + | *Force Sensors | ||
| + | *Gas Sensors | ||
| + | *Optical Sensors | ||
| + | *Sonar Range Finders | ||
| + | *Temperature and Humidity Sensors | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Vectoring Robots]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Mechanical Engineering]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Programmable Robots]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 12:44, 21 April 2021
Vectoring robots are robots that are able to add left/right strafing to their motion. In other words, vectoring robots can move sideways. Conventional wheeled mobile robots can only move forward and backwards and turn left/right. By adding the left and right strafing components, vectoring robots are able to move in any direction along the ground and turn left/right. This is accomplished by equipping special wheels and using a microcontroller to calculate the motor speeds required for a commanded motion.
Contents
How Vectoring Movement is Possible
Vectoring movement is achieved through a sum of forces generated by each wheel. In Figure 1 below, you will notice that for the robot to move to the right motor A will need to move in the negative direction and motors B and C would move in the positive direction.
This diagram also shows why motors B and C must be reduced while moving sideways. Motors B and C must have the same power to negate the forward and back movement while motor A must generate the same amount of sideways force as the sum of B and C.
Figures 2 and 3 show the two distinct types of omni wheels. Both Omni wheels and Mecanum wheels provide traction in normal wheel movement as any other wheel would. however, what makes these wheels special are the small rollers along the wheel's edges. These wheels are designed to provide a minimum amount of friction sideways allowing the wheels to move in any direction.
Omni wheels have smaller rollers on the edges that move completely perpendicular to the wheel itself. With this type of wheel they must be mounted perpendicular to the center of the robot as seen in Figure 1.
Mecanum wheels are unique in that the small rollers are at a 45 degree angle. This allows them to be mounted like normal wheels but provide the same style of movement as Omni wheels.
4WD Omni-directional Robots
We have several options for four wheel omni-directional robots. They use mecanum wheels or omni wheels mounted at a 45 degree angle. By changing the speeds and directions of the wheels you can achieve movement in any direction! Due to the style of the wheels it is possible to move the wheels in a standard "tank style" motion to drive normally when needed. These robots also work well for supporting high payloads since the wheels allow them to turn with very low friction. See the load ratings on the robot page for an idea of the payload.
4WD Vectoring Robot Platforms
- Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 DM
- Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 SB
- Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG42 SB
- Programmable Mecanum Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG52 DB
- Programmable Quad-Wheel Omni-Directional Vectoring Robot Kit - IG32 SB
3WD Omni-directional Robots
Our 3WD omni-directional robots use our double-row omni wheels, allowing them to vector in any direction. 3WD Vectoring Robot Platform
- Programmable Tri-Wheel Vectoring Robot Kit - IG32 Medium Duty SB
- Programmable Triangular Omni Wheel Vectoring Robot - IG32 DM
Controls and Specifications
Motors and Motor Mounts
We have mecanum wheel robot kits that use IG32, IG42, and IG52 motors. Below are the motors that we recommend using with these platforms, though you can use different motors if you need more speed or higher payloads. All motors are available in wide range of RPMs and some are available with a built in encoder option. For a detailed list of our available motors please see the link below. The Omni wheel based chassis is available in both IG32 and IG42 variants.
Suggested Motors
- 32mm 190 RPM 24V IG32 Gear Motor (TD-015-190)
- 42mm 240 RPM 24V IG42 Gear Motor (TD-016-240)
- 52mm 136 RPM 24V IG52 Gear Motor (TD-048-136)
- IG32 or IG42 Motor Mount Tube for Omni Wheel Chassis (TD-056-342)
Motor Hookups
Click here for a listing of our available motors.
Wheels and Drive Shafts
Our Mecanum wheels are available stand-alone or paired with compatible wheel hubs. All wheels listed below fit any of the nexus aluminum hubs. The 4" mecanum wheels also fit the SDR manufactured flush mounted hubs.
- 4 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel - Ball Bearing(TD-090-100)
- 4 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel - Sleeve Bearing(TD-169-100)
- 6 inch nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel (TD-090-152)
- 8 inch Nexus Robot Aluminum Mecanum Wheel (TD-090-203)
- SDR Flush Mounted Hub with 6mm Bore (TD-107-006)
- SDR Flush Mounted Hub with 8mm Bore (TD-107-008)
Nexus Aluminum Hubs
- 6mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-006)
- 8mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-008)
- 12mm Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-012)
- 0.5" Bore - Nexus Aluminum Wheel Hub (TD-094-050)
The Omni wheels are shafts are sold together as one unit. The shaft comes with a bearing and lock collar that fit into/onto the motors and motor mounts. The wheels are 4 inch in diameter. The traction wheels are made of durable urethane to help grip the floor. The wheels are available in two types; single row and double row. The double row wheels provide smoother operation but both work great.
- Nexus Omni-Wheel and Shaft Assembly - 6mm Bore (TD-145-006)
- Nexus Omni-Wheel and Shaft Assembly - 8mm Bore (TD-145-008)
Mecanum Wheels
Below is a diagram showing how the mecanum wheels should be mounted and which direction to turn the wheels for vectoring movements.
Motor and Speed Controllers
We offer a variety of motor controllers to allow for simple operation of the robot. The motor controllers are independent of the chassis type (Mecanum or Omni). To provide vectoring movement it is required to have one motor channel per motor. Higher amperage motor controllers will be needed as the motor size and payload of the robot increases.
For the best vectoring performance, use motors with encoders and a motor controller that has closed loop speed control, such as a Roboteq or Roboclaw. To vector cleanly in a desired direction, the robot's wheels must rotate at precise speed ratios relative to one another. If the ratios are off, then the movement will be sloppy -- e.g. instead of strafing purely to the right the robot might also drift slightly forward and turn slightly left during the movement. Closed loop speed control mitigates this effect so the robot moves as commanded.
Dimension Engineering's motor controllers are versatile and reliable options when no closed loop speed control is needed.
Recommended Motor Controllers
- RoboClaw 2x15A (TE-331-215)
- RoboClaw 2x30A (TE-331-230)
- RoboClaw Solo 30A Motor Controller (TE-331-130)
- RoboteQ SDC2160 2x20A (TE-144-060)
- SyRen 10 (TE-098-110)
- Sabertooth Dual 25A (TE-091-225)
- Sabertooth Dual 32A (TE-091-232)
Controller and Controller Interface
We offer three main control options for vectoring robots: Radio Controlled, WiFi, and wireless serial (xBee).
R/C (Radio Control)
For R/C control of the robot, although the motor controllers listed above support RC you will still need a microcontroller on the robot in order to handle the motor mixing necessary to achieve vectoring motion.
For accurate robot control, the remote will require at least a two axis joystick/control and a signal switch to change driving modes if desired. Below is a recommended listing of our R/C remotes.
- FLYSKY FS-i6 2.4G 6CH Transmitter & Receiver (TE-328-000)
- Spektrum DSMX DX6e Transmitter with AR620 Receiver (TE-336-DX6)
- Spektrum DSMX DX8 8-Channel Transmitter Gen 2 with AR8010T Receiver (TE-113-008)
WiFi Control
We offer an Arduino-based Wifi control interface package (TE-900-003) that includes an Arduino Mega, SDR Breakout shield, Raspberry Pi, voltage regulators, and a 4 channel TTL Relay Board (TE-010-405). The control package also comes with the source code for the control software and the Arduino firmware needed for operation of the robot.
Please see our WiFi Control Interface Support Page for more information.
Wireless Serial Control
Wireless serial control is achieved through an xBee radio. Wireless serial is currently only available if you choose an Arduino-based control system. The xBee radio connects to the Arduino through the Arduino Wireless SD Shield (MCU-064-000). A Wireless Serial Control system is available by request. Please contact us for more information.
Please see our Wireless Serial Support Page for more information.
Hardware
The final item you need to make your kit complete is a hardware package. It includes nuts, bolts, washers, cable ties, and cable hold downs.
- Hardware Package (mounts most components to the base robot) (TD-021-000)
- Servo Standoff Mounting Hardware (TD-024-000)
Sensors
In order to make your robot autonomous, you will need to add sensors. Sensors can always be added or removed at a later date but always be mindful of how the sensors interact with your microcontroller. Some sensors operate under I2C, some SPI and some analog. See our Sensor Support Page for more information.
- Accelerometers, Gyros, GPS, and Compasses
- Contact Sensors
- Current Sensors
- Force Sensors
- Gas Sensors
- Optical Sensors
- Sonar Range Finders
- Temperature and Humidity Sensors